C8 Glossary of website basics
Download PDF Version
1. Introduction
This guide provides some useful explanations of the most commonly used terms when having a website.
2. Seven basic terms explained
2.1 What is the Internet?
Established in the 1950s, the Internet is a massive network of networks that can store data.
2.2 What is the World Wide Web (WWW)?
Established in the 1990s by Sir Tim Berners-Lee, the WWW is the protocol or ‘language’ which allows us to access that data over the Internet and do all the things we can, such as viewing websites, emailing, watching videos, etc. If we were to liken the Internet to a computer that stores data, the WWW would be the operating system (eg Windows 8).

2.3 What is a browser?
A browser is the system that helps you look at or “browse” the internet. Internet Explorer, Google Chrome and Firefox are by far the most popular browsers. If you were to liken the WWW to an operating system, browsers would be the software that translates the WWW into a useable format.
2.4 What is a Search engine?

A Search engine is the system that is used specifically to search for things on the internet. In the UK, Google is used for nearly 90% of searches, so the terms “Google” and “search engine” have almost become synonymous with each other. You can increase your chances of getting picked up by search engines by following some simple tips which we provide in Cliktips Guide C4 Search engines and how to optimise your site.
2.5 What is a web site?
A web site is a location on the WWW. It is hosted on at least one web server and is (typically) accessible via the internet through an internet address.
2.6 What is a domain name?
A domain name is the primary address of a website, eg www.joebloggs.com. Some people confuse the domain name with the website itself but they are two different entities. Please note:
In practice the domain name usually leads to the home page of the website.
You can buy your own domain name through us and our system will automatically link it to your site.
Or if you already have one, you can update its settings (with whoever you bought it from) so that it is linked to your ClikBeats site. So there is no need to transfer it to us.
2.7 What does ‘URL’ mean
A URL or “uniform resource locator” is the address of a specific part of a web site, eg www.joebloggs.com/aboutme (the URL of the home page would be www.joebloggs.com).
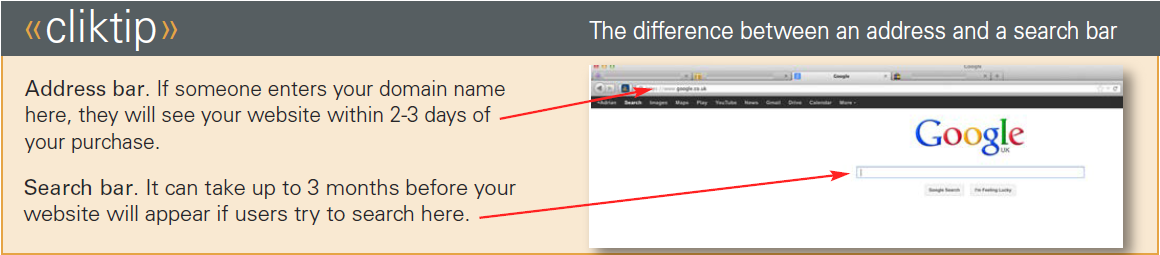
3. Some other useful terms
Blog. An online diary regularly updated by an individual or group with topical news and events.
Content management system (CMS). An online tool for updating websites such as the ClikBeats system. We use the term Admin system, but in essence it is the same thing as a CMS.
Ecommerce. A general term relating to the buying and selling of goods and services via the internet, usually involving online payment.
Hit. In practice, a click made on a web site. A hit is recorded for each graphic or block of text requested from a web server. For various reasons, it is not a reliable measure of the number of people viewing a page.
HTML. ‘Hyper Text Markup Language’ is the language (or type of coding) that programmers use when building websites. It is written in the form of elements consisting of tags enclosed in brackets. For example, if you were to bold some text in our admin system, you would notice that it puts the tag <b> at the start of the text and </b> at the end. If you were to change the ‘b’ to an ‘i’ then it would put it in italics. This is HTML in its most basic form.
HTML5. The same as html but compatible with portable devices such as mobile phones and tablets with added features such as video playback, animations etc.
HTTP. The WWW uses a ‘protocol’ for communicating data around the Internet. This is based on the exchange or transfer of ‘hypertext’ files, text files that can link to each other using ‘hyperlinks’. ‘HTTP’ is the name given to this protocol and stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol .
IP address. The unique address a server uses to host information. In effect this is your web address but in number format, eg 204.51.149.43. This is hardly user friendly which is why we have domain names.
Portal. A website that acts as a gateway to information on the internet.
PPC (pay per click). PPC is a method of charging advertisers, so whenever a user clicks on an online advertisement the advertiser is charged. Google, Facebook, YouTube, etc, all operate PPC schemes.
Search engine optimisation. A structured marketing approach used to increase the relative ranking position of a company or its products in search engine listings.
Social media. Digital media (typically websites) which encourage audience participation, interaction and sharing, such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, etc.
SPAM. Unsolicited email, usually sent in bulk and to an untargeted audience.
4. Further reading
Here are some useful websites if you would like to find out more.

